[Python] 적절한 샘플 사이즈를 찾아주는 코드
2021. 1. 1. 00:46ㆍ분석 Python/구현 및 자료
728x90
모집단이 클 경우에는 샘플링을 통해 시각화를 위해서나 통계치를 뽑아줘야 할 것이다.
이때 가장 적절한 샘플사이즈를 알려주는 코드가 있어서 공유한다.
그리고 각각에 대해서 분포별로 실험을 진행해봤다.
def sampleSize(
population_size,
margin_error=.05,
confidence_level=.99,
sigma=1/2
):
"""
Calculate the minimal sample size to use to achieve a certain
margin of error and confidence level for a sample estimate
of the population mean.
Inputs
-------
population_size: integer
Total size of the population that the sample is to be drawn from.
margin_error: number
Maximum expected difference between the true population parameter,
such as the mean, and the sample estimate.
confidence_level: number in the interval (0, 1)
If we were to draw a large number of equal-size samples
from the population, the true population parameter
should lie within this percentage
of the intervals (sample_parameter - e, sample_parameter + e)
where e is the margin_error.
sigma: number
The standard deviation of the population. For the case
of estimating a parameter in the interval [0, 1], sigma=1/2
should be sufficient.
"""
alpha = 1 - (confidence_level)
# dictionary of confidence levels and corresponding z-scores
# computed via norm.ppf(1 - (alpha/2)), where norm is
# a normal distribution object in scipy.stats.
# Here, ppf is the percentile point function.
zdict = {
.90: 1.645,
.91: 1.695,
.99: 2.576,
.97: 2.17,
.94: 1.881,
.93: 1.812,
.95: 1.96,
.98: 2.326,
.96: 2.054,
.92: 1.751
}
if confidence_level in zdict:
z = zdict[confidence_level]
else:
from scipy.stats import norm
z = norm.ppf(1 - (alpha/2))
N = population_size
M = margin_error
numerator = z**2 * sigma**2 * (N / (N-1))
denom = M**2 + ((z**2 * sigma**2)/(N-1))
return int(numerator/denom)
노말 분포
population_sizes = np.arange(100,10000,1000)
num_plots = len(population_sizes)
total_cols = 4
total_rows = num_plots//total_cols + 1
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=total_rows, ncols=total_cols,
figsize=(7*total_cols, 7*total_rows), constrained_layout=True)
for i , population_size in enumerate(population_sizes):
row = i//total_cols
pos = i % total_cols
population_ = np.random.normal(size=population_size)
sample_ = np.random.choice(population_, sampleSize(population_size))
sns.distplot(population_,ax=axs[row][pos])
sns.distplot(sample_,ax=axs[row][pos])
axs[row][pos].set_title(f"population size : {population_size}",size=30)
if total_rows * total_cols > len(population_sizes) :
remainder_n = total_rows * total_cols - len(population_sizes)
for i in range(remainder_n) :
axs[row][-(i+1)].axis("off")
plt.show()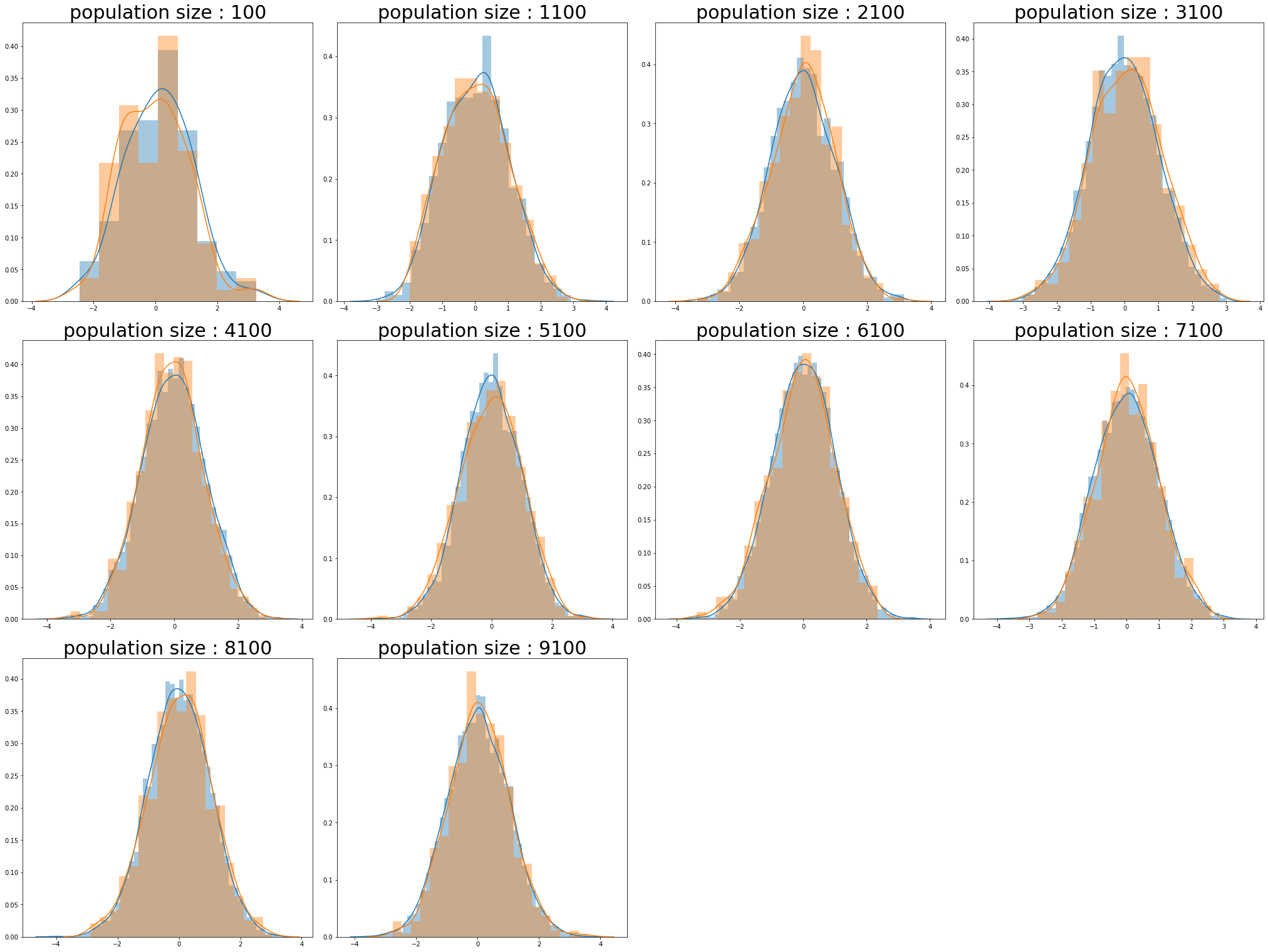
베타 분포 -1
population_sizes = np.arange(100,10000,1000)
num_plots = len(population_sizes)
total_cols = 4
total_rows = num_plots//total_cols + 1
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=total_rows, ncols=total_cols,
figsize=(7*total_cols, 7*total_rows), constrained_layout=True)
for i , population_size in enumerate(population_sizes):
row = i//total_cols
pos = i % total_cols
population_ = np.random.beta(a=0.5,b=0.5,size=population_size)
sample_ = np.random.choice(population_, sampleSize(population_size))
sns.distplot(population_,ax=axs[row][pos])
sns.distplot(sample_,ax=axs[row][pos])
axs[row][pos].set_title(f"population size : {population_size}",size=30)
if total_rows * total_cols > len(population_sizes) :
remainder_n = total_rows * total_cols - len(population_sizes)
for i in range(remainder_n) :
axs[row][-(i+1)].axis("off")
plt.show()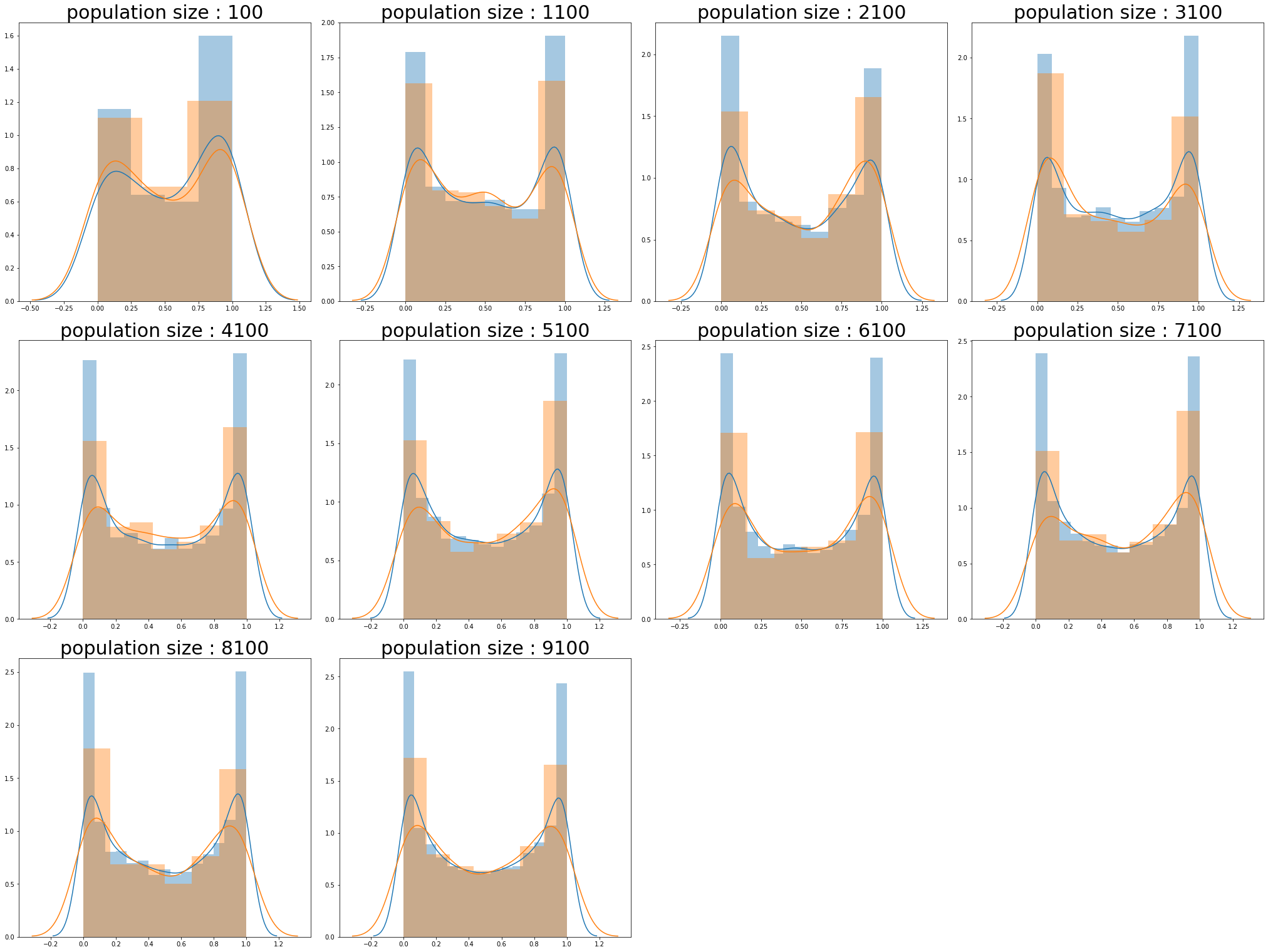
베타 분포 -2
population_sizes = np.arange(100,10000,1000)
num_plots = len(population_sizes)
total_cols = 4
total_rows = num_plots//total_cols + 1
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=total_rows, ncols=total_cols,
figsize=(7*total_cols, 7*total_rows), constrained_layout=True)
for i , population_size in enumerate(population_sizes):
row = i//total_cols
pos = i % total_cols
population_ = np.random.beta(a=0.9,b=0.5,size=population_size)
sample_ = np.random.choice(population_, sampleSize(population_size))
sns.distplot(population_,ax=axs[row][pos])
sns.distplot(sample_,ax=axs[row][pos])
axs[row][pos].set_title(f"population size : {population_size}",size=30)
if total_rows * total_cols > len(population_sizes) :
remainder_n = total_rows * total_cols - len(population_sizes)
for i in range(remainder_n) :
axs[row][-(i+1)].axis("off")
plt.show()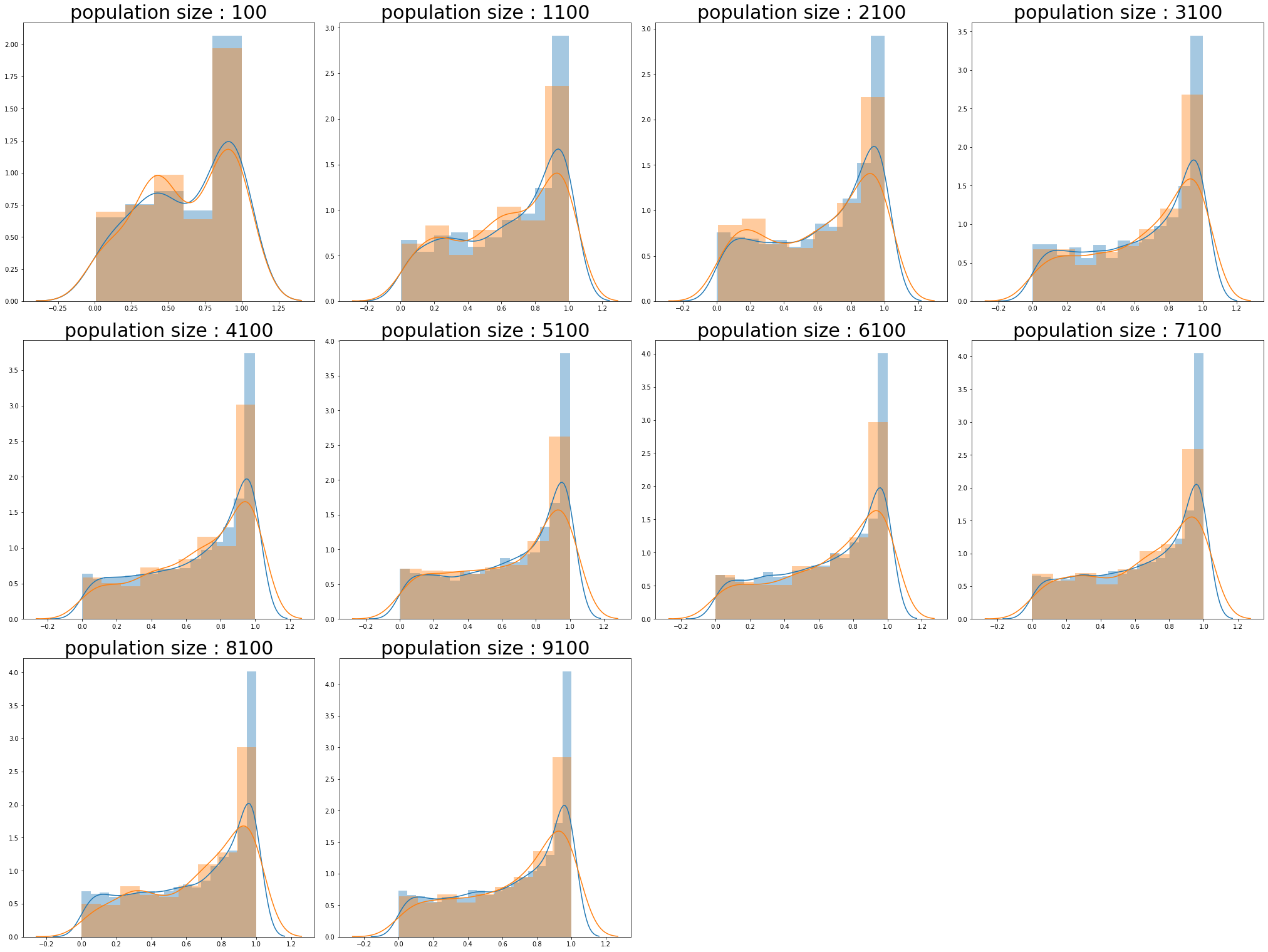
mixture distribution
population_sizes = np.arange(100,10000,1000)
num_plots = len(population_sizes)
total_cols = 4
total_rows = num_plots//total_cols + 1
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=total_rows, ncols=total_cols,
figsize=(7*total_cols, 7*total_rows), constrained_layout=True)
for i , population_size in enumerate(population_sizes):
row = i//total_cols
pos = i % total_cols
mean = (-4, 2)
cov = [[1, 0], [0, 1]]
population_ = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, size=population_size).reshape(-1,)
sample_ = np.random.choice(population_, sampleSize(population_size))
sns.distplot(population_,ax=axs[row][pos])
sns.distplot(sample_,ax=axs[row][pos])
axs[row][pos].set_title(f"population size : {population_size}",size=30)
if total_rows * total_cols > len(population_sizes) :
remainder_n = total_rows * total_cols - len(population_sizes)
for i in range(remainder_n) :
axs[row][-(i+1)].axis("off")
plt.show()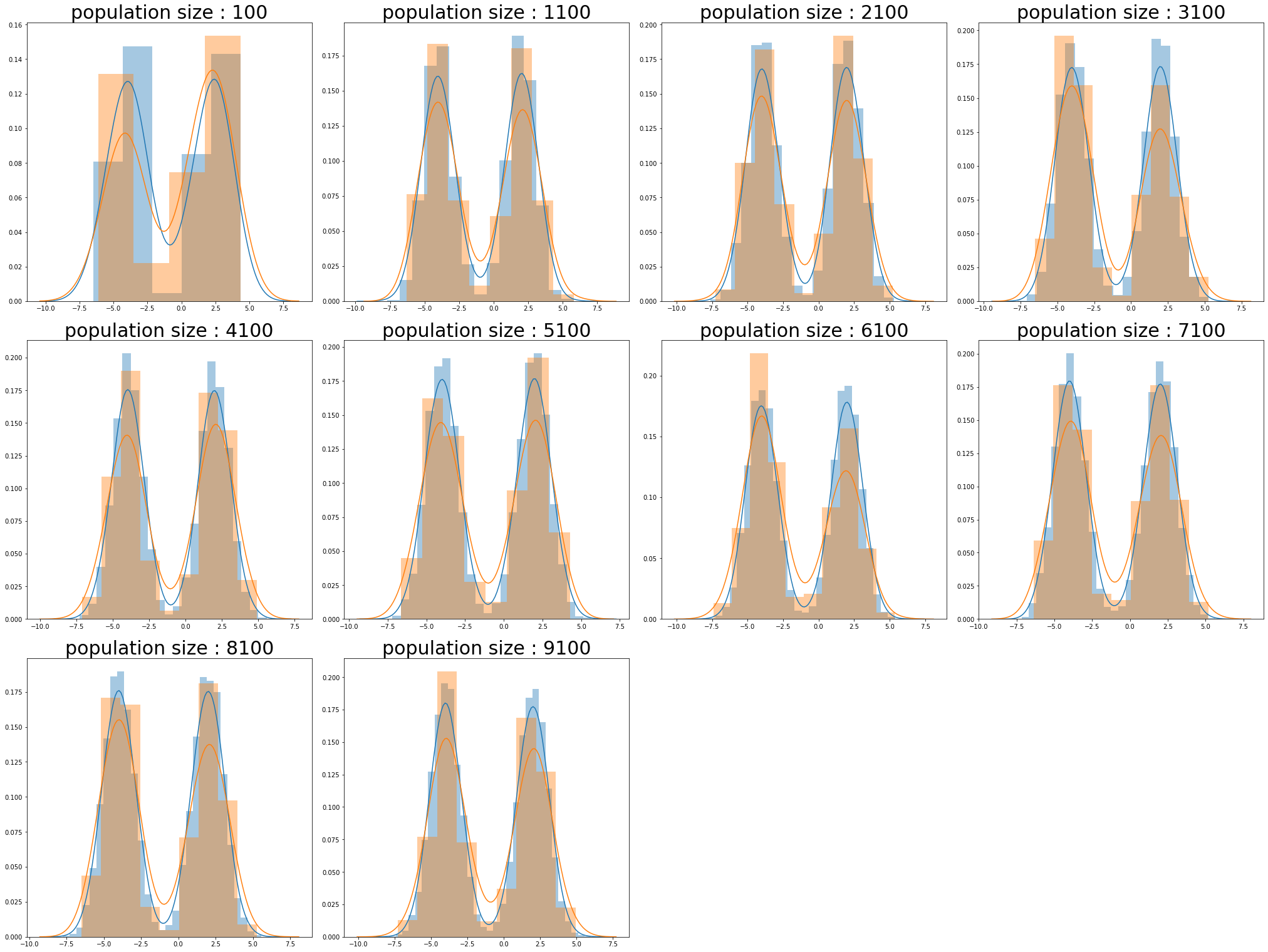
728x90
'분석 Python > 구현 및 자료' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Python] Icecream 패키지를 사용하여 디버깅하기 (0) | 2021.01.16 |
|---|---|
| [Python] itertools (0) | 2021.01.01 |
| [Jupyter] GPU 사용량 주기적으로 체크하는 코드 (0) | 2021.01.01 |
| [Python] Wordcloud Example (0) | 2020.12.31 |
| [TIP] Class에 사전(dict)으로 property 추가하는 법 (0) | 2020.12.18 |