728x90
유용한 함수들을 발견하게 되면 정리해보기
개인적으로 중요하다고 생각하는 것에 ★ 표시
import torch
import numpy as npFunction 1 — torch.tensor
t1 = torch.tensor([[21,39],[31,30],[23,43],[11,46],[26,46],[31,25],[21,38],[22,39],[22,19],[18, 14]])
t1
t2 = torch.tensor([])
t2
t2.size()

Function 2 — torch.from_numpy
a1 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
a1.dtype
t1 = torch.from_numpy(a1)
t1.dtype
Hight_Weight = np.array([[161,67],[154,76],[172, 61]])
Heart_Rate = np.array([78,89,72])
(Hight_Weight.dtype, Heart_Rate.dtype)
l2 = (Hight_Weight, Heart_Rate)
for i in l2 :
tensor = torch.from_numpy(i)
print("Type of the element\n {}\n is {}\n".format(i, tensor.dtype))

A NumPy array containing string elements cannot be converted to a tensor. The only supported types for a tensor are : float64, float32, float16, complex64, complex128, int64, int32, int16, int8, uint8, and bool.
Function 3 — tensor.unbind ★
(유용하다고 생각)
t1 = torch.randn(3,3)
t1
t1.unbind()
t1.unbind(dim=1)
Function 4 — torch.where ★
(유용하다고 생각)
x = torch.tensor([[1,2,3], [-4,-5,-6], [7,8,9]])
y = torch.tensor(torch.mul(x, -1)) # Elementwise negative of x
torch.where(x>0, x, y)
x = torch.tensor([8, 4, 5, 6, 1, 9, 10, 1, 10, 7])
y = torch.tensor([2, 3, 3, 10, 10 , 4, 5, 6, 7 ,6])
torch.where( x>y, x, y)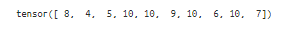
Function 5 — torch.trapz ★
(중요하다고 생각)
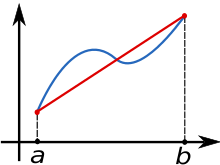
This function estimates the definite integral of y with respect to x along the given dimension, based on 'Trapezoidal rule'.
The arguments required are :
- y : A tensor containing values of the function to integrate. (blue line in the illustration below)
- x : The points at which the function y is sampled. (x axis in the illustration below)
- Dimension for integration
y = torch.randn(2,2)
x = torch.tensor([[1,2],[2,3]])
torch.trapz(y,x)
y = torch.randn(3,3)
torch.trapz(y, dx = 1)
$y=x^2$ (1,2,3,4,5)
적분 하기
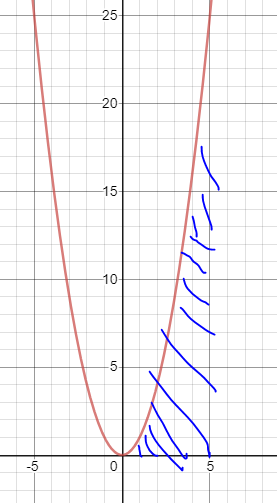
Y = torch.tensor([1 ,4, 9, 16, 25])
torch.trapz(Y)
Y = torch.tensor([[1 ,4, 9, 16, 25],
[1 ,4, 9, 16, 25],
[1 ,4, 9, 16, 25]
])
torch.trapz(Y,dim=0)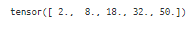

Deep Learning requires a lot of calculus to know more about the models that are being used.
torch.trapz() makes our job of finding estimated integral easy.
Function 6 — torch.eye
torch.eye(n=4, m=5)
torch.eye(n=3)

Function 7 — torch.full
torch.full(size=(3,2), fill_value=10)
torch.full(size=[2, 3, 4], fill_value=5)

Function 8 — torch.cat ★
(자주 사용)
a = torch.ones(3,2)
b = torch.zeros(3,2)
torch.cat((a, b)) # default dim=0
Output:
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]])
x = torch.full((3,3), fill_value=4)
y = torch.full((3,3), fill_value=7)
torch.cat((x, y), dim=1)
Output:
tensor([[4., 4., 4., 7., 7., 7.],
[4., 4., 4., 7., 7., 7.],
[4., 4., 4., 7., 7., 7.]])Function 9 — torch.take
return : 1D tensor
# 1D input Tensor
b = torch.tensor([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
torch.take(b, torch.tensor([2]))
Output:
tensor([30])
# 2D input tensor
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
torch.take(a, torch.tensor([3,4]))
Output:
tensor([4, 5])
Function 10 — torch.Tensor.clone
a = torch.tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.],
[5., 6.]])
b = a
a[1,0]=9
b
Output:
tensor([[1., 2.],
[9., 4.],
[5., 6.]])Function 11 — torch.view
# Example 1 - working
random_tensor = torch.arange(1., 17.)
print(random_tensor)
random_tensor.view(8,2)
tensor([ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14.,
15., 16.])
tensor([[ 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4.],
[ 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8.],
[ 9., 10.],
[11., 12.],
[13., 14.],
[15., 16.]])
z = x.view(-1, 8)Function 12 — torch.trace
$1+6+11+16 = 34$
# Example 1 - working
random_tensor = torch.arange(1., 17.).view(4,4)
print(random_tensor)
torch.trace(random_tensor)
tensor([[ 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8.],
[ 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[13., 14., 15., 16.]])
tensor(34.)Function 13 — torch.gather
torch.gather(input, dim, index) -> Tensor
Gather values alogs an axis specified by dim. loop over the dimension and for each element with take the tensor index by index.
t = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
torch.gather(t, 1, torch.tensor([[0,0],[1,0]]))
tensor([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4]])
-->
tensor([[ 1, 1],
[ 4, 3]])
Reference
towardsdatascience.com/5-powerful-pytorch-functions-that-every-beginner-should-know-e75cb26ec8bc
'분석 Python > Pytorch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Pytorch] Error : Leaf variable has been moved into the graph interior 해결 방법 공유 (0) | 2021.01.16 |
|---|---|
| [Pytorch] How to Apply the Weight Initialization (Code) (0) | 2020.12.17 |
| PyTorch Lighting + Ray tune (0) | 2020.11.07 |
| [TIP / Pytorch] torch class name 얻는 방법 (0) | 2020.10.31 |
| [TIP / Pytorch] calculate convolution output shae (conv2d , pooling) (Conv 아웃풋 값 (0) | 2020.10.31 |